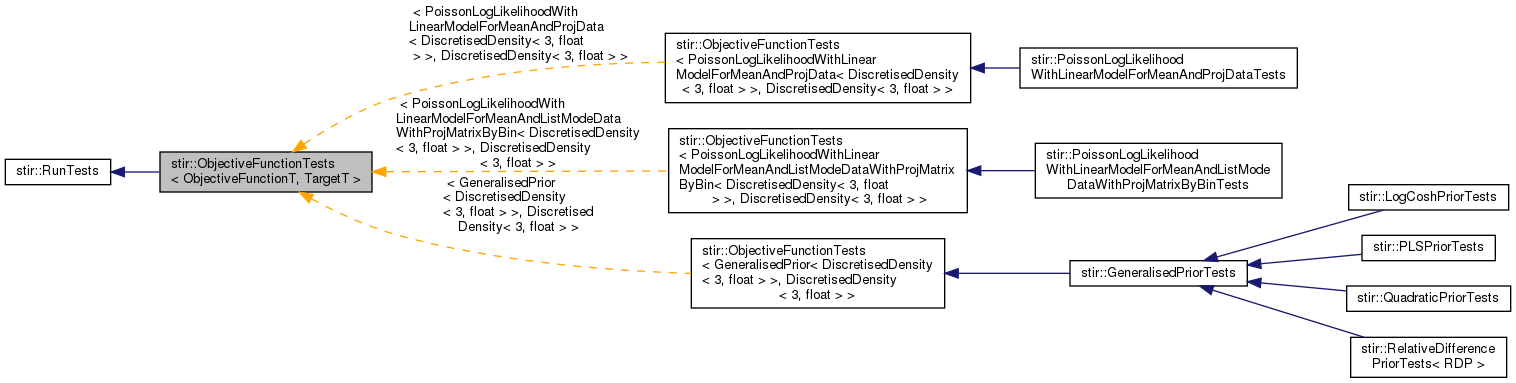
Test class for GeneralisedObjectiveFunction and GeneralisedPrior. More...
#include "stir/recon_buildblock/test/ObjectiveFunctionTests.h"
Public Types | |
| typedef ObjectiveFunctionT | objective_function_type |
| typedef TargetT | target_type |
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual Succeeded | test_gradient (const std::string &test_name, ObjectiveFunctionT &objective_function, TargetT &target, const float eps, const bool full_gradient=true) |
| Test the gradient of the objective function by comparing to the numerical gradient via perturbation. More... | |
| virtual Succeeded | test_Hessian (const std::string &test_name, ObjectiveFunctionT &objective_function, const TargetT &target, const float eps) |
| Test the accumulate_Hessian_times_input of the objective function by comparing to the numerical result via perturbation. More... | |
| virtual Succeeded | test_Hessian_concavity (const std::string &test_name, ObjectiveFunctionT &objective_function, const TargetT &target, const float mult_factor=1.F) |
| Test the Hessian of the objective function by testing the (mult_factor * x^T Hx > 0) condition. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from stir::RunTests Public Member Functions inherited from stir::RunTests | |
| RunTests (const double tolerance=1E-4) | |
| Default constructor. | |
| virtual | ~RunTests () |
| Destructor, outputs a diagnostic message. | |
| virtual void | run_tests ()=0 |
| Function (to be overloaded) which does the actual tests. More... | |
| bool | is_everything_ok () const |
| Returns if all checks were fine upto now. | |
| int | main_return_value () const |
| Handy return value for a main() function. More... | |
| void | set_tolerance (const double tolerance) |
| Set value used in floating point comparisons (see check_* functions) | |
| double | get_tolerance () const |
| Get value used in floating point comparisons (see check_* functions) | |
| bool | check (const bool, const std::string &str="") |
| Tests if true, str can be used to tell what you are testing. More... | |
| template<class T1 , class T2 > | |
| bool | check_if_less (T1 a, T2 b, const std::string &str="") |
| check if a<b | |
| bool | check_if_equal (const std::string &a, const std::string &b, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_equal (const double a, const double b, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_equal (const short a, const short b, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_equal (const unsigned short a, const unsigned short b, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_equal (const int a, const int b, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_equal (const unsigned int a, const unsigned int b, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_equal (const long a, const long b, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_equal (const unsigned long a, const unsigned long b, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_equal (const Bin &a, const Bin &b, const std::string &str="") |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | check_if_equal (const DetectionPosition< T > &a, const DetectionPosition< T > &b, const std::string &str="") |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | check_if_equal (const std::complex< T > a, const std::complex< T > b, const std::string &str="") |
| check equality by calling check_if_equal on real and imaginary parts | |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | check_if_equal (const VectorWithOffset< T > &t1, const VectorWithOffset< T > &t2, const std::string &str="") |
| check equality by comparing ranges and calling check_if_equal on all elements | |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | check_if_equal (const std::vector< T > &t1, const std::vector< T > &t2, const std::string &str="") |
| check equality by comparing size and calling check_if_equal on all elements | |
| bool | check_if_equal (const ProjDataInMemory &t1, const ProjDataInMemory &t2, const std::string &str="") |
| template<int n> | |
| bool | check_if_equal (const IndexRange< n > &t1, const IndexRange< n > &t2, const std::string &str="") |
| template<int num_dimensions, class coordT > | |
| bool | check_if_equal (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, coordT > &a, const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, coordT > &b, const std::string &str="") |
| check equality by comparing norm(a-b) with tolerance | |
| bool | check_if_zero (const double a, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_zero (const short a, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_zero (const unsigned short a, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_zero (const int a, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_zero (const unsigned int a, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_zero (const long a, const std::string &str="") |
| bool | check_if_zero (const unsigned long a, const std::string &str="") |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | check_if_zero (const VectorWithOffset< T > &t, const std::string &str="") |
| use check_if_zero on all elements | |
| template<int num_dimensions, class coordT > | |
| bool | check_if_zero (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, coordT > &a, const std::string &str="") |
| compare norm with tolerance | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual shared_ptr< const TargetT > | construct_increment (const TargetT &target, const float eps) const |
| Construct small increment for target. More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from stir::RunTests Protected Member Functions inherited from stir::RunTests | |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | check_if_equal_generic (const T &a, const T &b, const std::string &str) |
| function that is called by some check_if_equal implementations. It just uses operator!= | |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | check_if_zero_generic (T a, const std::string &str) |
| function that is called by some check_if_zero implementations. It just uses operator!= | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from stir::RunTests Protected Attributes inherited from stir::RunTests | |
| double | tolerance |
| tolerance for comparisons with real values | |
| bool | everything_ok |
| variable storing current status | |
Detailed Description
template<class ObjectiveFunctionT, class TargetT>
class stir::ObjectiveFunctionTests< ObjectiveFunctionT, TargetT >
Test class for GeneralisedObjectiveFunction and GeneralisedPrior.
This contains some numerical tests to check gradient and Hessian calculations.
Note that the test only works if the objective function is well-defined. For example, if certain projections are non-zero, while the model estimates them to be zero, the Poisson objective function is in theory infinite. ObjectiveFunction uses some thresholds to try to avoid overflow, but if there are too many of these bins, the total objective function will become infinite. The numerical gradient then becomes ill-defined (even in voxels that do not contribute to these bins).
Member Function Documentation
◆ test_gradient()
|
virtual |
Test the gradient of the objective function by comparing to the numerical gradient via perturbation.
If full_gradient=true, all elements in the gradient are tested (using single-element increments). This is slow. Otherwise, the test checks that 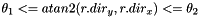 . dx is computed via construct_increment().
. dx is computed via construct_increment().
Note: target is non-const, as the code will add/subtract eps, but the actual values are not modified after the test exits.
◆ test_Hessian()
|
virtual |
Test the accumulate_Hessian_times_input of the objective function by comparing to the numerical result via perturbation.
This test checks that 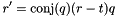 . dx is computed via construct_increment().
. dx is computed via construct_increment().
◆ test_Hessian_concavity()
|
virtual |
Test the Hessian of the objective function by testing the (mult_factor * x^T Hx > 0) condition.
setup images
Compute H x
Compute dot(x,(H x))
◆ construct_increment()
|
protectedvirtual |
Construct small increment for target.
Result is eps*(target / target.find_max() + 0.5), i.e. it is always positive (if target is non-negative).
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- /home/sirfuser/devel/STIRdistrib/STIR/src/include/stir/recon_buildblock/test/ObjectiveFunctionTests.h
 1.8.13
1.8.13