This abstract class is the basis for all image representations. More...
#include "stir/DiscretisedDensity.h"
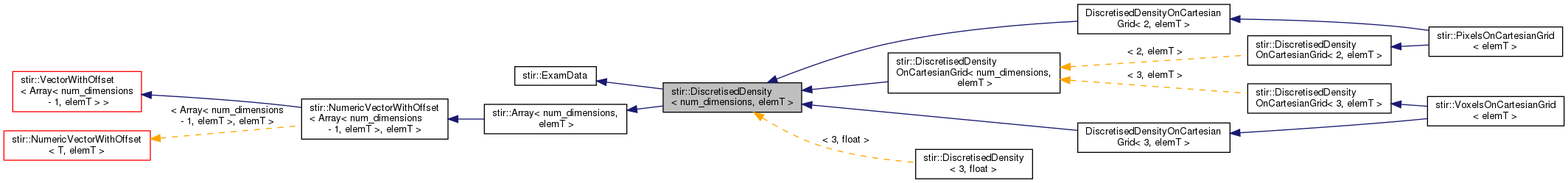
Public Types | |
| typedef DiscretisedDensity< num_dimensions, elemT > | hierarchy_base_type |
| A typedef that can be used what the base of the hierarchy is. More... | |
 Public Types inherited from stir::Array< num_dimensions, elemT > Public Types inherited from stir::Array< num_dimensions, elemT > | |
| typedef base_type::value_type | value_type |
typedefs such that we do not need to have typename wherever we use these types defined in the base class | |
| typedef base_type::reference | reference |
| typedef base_type::const_reference | const_reference |
| typedef base_type::difference_type | difference_type |
| typedef base_type::size_type | size_type |
| typedef base_type::iterator | iterator |
| typedef base_type::const_iterator | const_iterator |
| typedef elemT | full_value_type |
| typedef full_value_type * | full_pointer |
| typedef const full_value_type * | const_full_pointer |
| typedef full_value_type & | full_reference |
| typedef const full_value_type & | const_full_reference |
| typedef FullArrayIterator< typename base_type::iterator, typename Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT >::full_iterator, elemT, full_reference, full_pointer > | full_iterator |
| This defines an iterator type that iterates through all elements. | |
| typedef FullArrayIterator< typename base_type::const_iterator, typename Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT >::const_full_iterator, elemT, const_full_reference, const_full_pointer > | const_full_iterator |
| As full_iterator, but for const objects. | |
 Public Types inherited from stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > Public Types inherited from stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > | |
| typedef size_t | size_type |
| typedef Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > | value_type |
| typedef value_type & | reference |
| typedef const value_type & | const_reference |
| typedef ptrdiff_t | difference_type |
| typedef Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > * | iterator |
| typedef Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > const * | const_iterator |
| typedef std::reverse_iterator< iterator > | reverse_iterator |
| typedef std::reverse_iterator< const_iterator > | const_reverse_iterator |
Public Member Functions | |
| DiscretisedDensity () | |
| Construct an empty DiscretisedDensity. | |
| DiscretisedDensity (const IndexRange< num_dimensions > &range, const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &origin) | |
| Construct DiscretisedDensity from a given range of indices & origin. | |
| DiscretisedDensity (const shared_ptr< const ExamInfo > &exam_info_sptr, const IndexRange< num_dimensions > &range, const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &origin) | |
| Construct DiscretisedDensity from ExamInfo and a given range of indices & origin. | |
| const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > & | get_origin () const |
| Return the origin. | |
| void | set_origin (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &origin) |
| Set the origin. | |
| virtual DiscretisedDensity< num_dimensions, elemT > * | get_empty_copy () const =0 |
| Allocate a new DiscretisedDensity object with same characteristics as the current one. | |
| virtual DiscretisedDensity< num_dimensions, elemT > * | clone () const =0 |
| Allocate a new DiscretisedDensity object which is a copy of the current one. | |
| DiscretisedDensity< num_dimensions, elemT > * | get_empty_discretised_density () const |
| Allocate a new DiscretisedDensity object with same characteristics as the current one. | |
Translation between indices and physical coordinates | |
| CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | get_physical_coordinates_for_indices (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &indices) const |
Return the coordinates of the centre of the basis-function corresponding to indices. More... | |
| CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | get_physical_coordinates_for_indices (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > &indices) const |
| Return the coordinates of the centre of the basis-function corresponding to non-integer coordinate in 'physical' coordinates. More... | |
| CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | get_relative_coordinates_for_indices (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &indices) const |
Return the relative coordinates of the centre of the basis-function corresponding to indices. More... | |
| CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | get_relative_coordinates_for_indices (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > &indices) const |
| Return the relative coordinates of the centre of the basis-function corresponding to the non-integer coordinates in 'index' coordinates. More... | |
| BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > | get_indices_closest_to_physical_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &coords) const |
| Return the indices of the basis-function closest to the given point. More... | |
| BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > | get_indices_closest_to_relative_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &coords) const |
| Return the indices of the basis-function closest to the given point. More... | |
| BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > | get_index_coordinates_for_physical_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &coords) const |
| Return the indices of the basis-function closest to the given point. More... | |
| BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > | get_index_coordinates_for_relative_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &coords) const |
| Return the index-coordinates of the basis-function closest to the given point. More... | |
| BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > | get_index_coordinates_for_LPS_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &coords) const |
| Translation from LPS coordinates to continuous indices. | |
| CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | get_LPS_coordinates_for_physical_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &indices) const |
| Translation from physical to LPS coordinates. | |
| CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | get_LPS_coordinates_for_indices (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &indices) const |
| Translation from indices to LPS coordinates. | |
| CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | get_LPS_coordinates_for_indices (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > &indices) const |
| Translation from continuous indices to LPS coordinates. | |
| CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | get_physical_coordinates_for_LPS_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &coords) const |
| Translation from LPS coordinates to physical coordinates. | |
| BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > | get_indices_closest_to_LPS_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &coords) const |
| Translation from LPS coordinates to indices. | |
Equality | |
| bool | has_same_characteristics (self_type const &, std::string &explanation) const |
| Checks if the 2 objects have the same type, index range, origin etc. More... | |
| bool | has_same_characteristics (self_type const &) const |
| Checks if the 2 objects have the same type, index range, origin etc. More... | |
| bool | operator== (const self_type &) const |
| check equality (data has to be identical) More... | |
| bool | operator!= (const self_type &) const |
| negation of operator== | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from stir::ExamData Public Member Functions inherited from stir::ExamData | |
| ExamData () | |
| ExamData. More... | |
| ExamData (const shared_ptr< const ExamInfo > &_this_exam) | |
| virtual const ExamInfo & | get_exam_info () const |
| virtual shared_ptr< const ExamInfo > | get_exam_info_sptr () const |
| Get shared pointer to exam info. | |
| virtual void | set_exam_info (ExamInfo const &) |
| change exam info More... | |
| void | set_exam_info_sptr (shared_ptr< const ExamInfo > new_exam_info_sptr) |
 Public Member Functions inherited from stir::Array< num_dimensions, elemT > Public Member Functions inherited from stir::Array< num_dimensions, elemT > | |
| Array () | |
| Construct an empty Array. | |
| Array (const IndexRange< num_dimensions > &) | |
| Construct an Array of given range of indices, elements are initialised to 0. | |
| Array (const IndexRange< num_dimensions > &range, shared_ptr< elemT[]> data_sptr) | |
| Construct an Array pointing to existing contiguous data. More... | |
| Array (const base_type &t) | |
| Construct an Array from an object of its base_type. | |
| Array (const self &t) | |
| Copy constructor. | |
| ~Array () override | |
| virtual destructor, frees up any allocated memory | |
| Array (Array &&other) noexcept | |
| move constructor More... | |
| Array & | operator= (Array other) |
| assignment operator More... | |
| IndexRange< num_dimensions > | get_index_range () const |
| size_t | size_all () const |
| return the total number of elements in this array | |
| virtual void | resize (const IndexRange< num_dimensions > &range) |
| change the array to a new range of indices, new elements are set to 0 More... | |
| virtual void | grow (const IndexRange< num_dimensions > &range) |
| alias for resize() | |
| elemT | sum () const |
| return sum of all elements | |
| elemT | sum_positive () const |
| return sum of all positive elements | |
| elemT | find_max () const |
| return maximum of all the elements | |
| elemT | find_min () const |
| return minimum of all the elements | |
| void | fill (const elemT &n) |
Fill elements with value n. More... | |
| void | apply_lower_threshold (const elemT &l) |
| Sets elements below value to the value. | |
| void | apply_upper_threshold (const elemT &u) |
| Sets elements above value to the value. | |
| bool | is_regular () const |
| checks if the index range is 'regular' More... | |
| bool | get_regular_range (BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &min, BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &max) const |
find regular range, returns false if the range is not regular More... | |
| Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > & | operator[] (int i) |
| allow array-style access, read/write | |
| const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > & | operator[] (int i) const |
| array access, read-only | |
| elemT & | operator[] (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &c) |
| allow array-style access given a BasicCoordinate to specify the indices, read/write | |
| const elemT & | operator[] (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &c) const |
| array access given a BasicCoordinate to specify the indices, read-only | |
| template<typename elemT2 > | |
| STIR_DEPRECATED void | axpby (const elemT2 a, const Array &x, const elemT2 b, const Array &y) |
| void | xapyb (const Array &x, const elemT a, const Array &y, const elemT b) |
| set values of the array to x*a+y*b, where a and b are scalar | |
| void | xapyb (const Array &x, const Array &a, const Array &y, const Array &b) |
| set values of the array to x*a+y*b, where a and b are arrays | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | sapyb (const T &a, const Array &y, const T &b) |
| set values of the array to self*a+y*b where a and b are scalar or arrays | |
| template<int num_dimensions, typename elemT> | |
| Array (Array< num_dimensions, elemT > &&other) noexcept | |
| template<typename elemT2 > | |
| void | axpby (const elemT2 a, const Array &x, const elemT2 b, const Array &y) |
| full_iterator | begin_all () |
| start value for iterating through all elements in the array, see full_iterator | |
| const_full_iterator | begin_all () const |
| start value for iterating through all elements in the (const) array, see full_iterator | |
| const_full_iterator | begin_all_const () const |
| start value for iterating through all elements in the array, see full_iterator | |
| full_iterator | end_all () |
| end value for iterating through all elements in the array, see full_iterator | |
| const_full_iterator | end_all () const |
| end value for iterating through all elements in the (const) array, see full_iterator | |
| const_full_iterator | end_all_const () const |
| end value for iterating through all elements in the array, see full_iterator | |
| Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > & | at (int i) |
| const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > & | at (int i) const |
| elemT & | at (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &c) |
| const elemT & | at (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, int > &c) const |
| self & | operator+= (const self &x) |
| self & | operator-= (const self &x) |
| self & | operator*= (const self &x) |
| self & | operator/= (const self &x) |
| self & | operator+= (const elemT x) |
| self & | operator-= (const elemT x) |
| self & | operator*= (const elemT x) |
| self & | operator/= (const elemT x) |
| self | operator+ (const self &x) const |
| self | operator+ (const elemT x) const |
| self | operator- (const self &x) const |
| self | operator- (const elemT x) const |
| self | operator* (const self &x) const |
| self | operator* (const elemT x) const |
| self | operator/ (const self &x) const |
| self | operator/ (const elemT x) const |
| bool | is_contiguous () const |
| return if the array is contiguous in memory | |
| elemT * | get_full_data_ptr () |
| member function for access to the data via a elemT* More... | |
| const elemT * | get_const_full_data_ptr () const |
| member function for access to the data via a const elemT* More... | |
| void | release_full_data_ptr () |
| signal end of access to elemT* More... | |
| void | release_const_full_data_ptr () const |
| signal end of access to const elemT* More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from stir::NumericVectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT >, elemT > Public Member Functions inherited from stir::NumericVectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT >, elemT > | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset (const VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > &t) | |
| Constructor from an object of this class' base_type. | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset (const NumericVectorWithOffset &t) | |
| Constructor from an object of this class' base_type. | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset (NumericVectorWithOffset &&other) noexcept | |
| move constructor More... | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator= (const NumericVectorWithOffset &other) |
| assignment | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset | operator+ (const NumericVectorWithOffset &v) const |
| adding vectors, element by element | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset | operator+ (const elemT &v) const |
return a new vector with elements equal to the sum of the elements in the original and the elemT | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset | operator- (const NumericVectorWithOffset &v) const |
| subtracting vectors, element by element | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset | operator- (const elemT &v) const |
return a new vector with elements equal to the difference of the elements in the original and the elemT | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset | operator* (const NumericVectorWithOffset &v) const |
| multiplying vectors, element by element | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset | operator* (const elemT &v) const |
return a new vector with elements equal to the multiplication of the elements in the original and the elemT | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset | operator/ (const NumericVectorWithOffset &v) const |
| dividing vectors, element by element | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset | operator/ (const elemT &v) const |
return a new vector with elements equal to the division of the elements in the original and the elemT | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator+= (const NumericVectorWithOffset &v) |
adding elements of v to the current vector More... | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator+= (const elemT &v) |
adding an elemT to the elements of the current vector | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator-= (const NumericVectorWithOffset &v) |
subtracting elements of v from the current vector More... | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator-= (const elemT &v) |
subtracting an elemT from the elements of the current vector | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator*= (const NumericVectorWithOffset &v) |
multiplying elements of the current vector with elements of v More... | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator*= (const elemT &v) |
multiplying the elements of the current vector with an elemT | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator/= (const NumericVectorWithOffset &v) |
dividing all elements of the current vector by elements of v More... | |
| NumericVectorWithOffset & | operator/= (const elemT &v) |
dividing the elements of the current vector by an elemT | |
| STIR_DEPRECATED void | axpby (const elemT2 a, const NumericVectorWithOffset &x, const elemT2 b, const NumericVectorWithOffset &y) |
| void | axpby (const NUMBER2 a, const NumericVectorWithOffset &x, const NUMBER2 b, const NumericVectorWithOffset &y) |
| void | xapyb (const NumericVectorWithOffset &x, const elemT a, const NumericVectorWithOffset &y, const elemT b) |
| set values of the array to x*a+y*b, where a and b are scalar | |
| void | xapyb (const NumericVectorWithOffset &x, const NumericVectorWithOffset &a, const NumericVectorWithOffset &y, const NumericVectorWithOffset &b) |
| set the values of the array to x*a+y*b, where a and b are vectors | |
| void | sapyb (const T2 &a, const NumericVectorWithOffset &y, const T2 &b) |
| set the values of the array to self*a+y*b, where a and b are scalar or vectors | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > Public Member Functions inherited from stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > | |
| VectorWithOffset () | |
| Default constructor: creates a vector of length 0. | |
| VectorWithOffset (const int hsz) | |
Construct a VectorWithOffset of given length (initialised with T()) | |
| VectorWithOffset (const int min_index, const int max_index) | |
Construct a VectorWithOffset with offset min_index (initialised with T()) | |
| STIR_DEPRECATED | VectorWithOffset (const int hsz, Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > *const data_ptr, Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > *const end_of_data_ptr) |
| Construct a VectorWithOffset of given length pointing to existing data. More... | |
| STIR_DEPRECATED | VectorWithOffset (const int min_index, const int max_index, Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > *const data_ptr, Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > *const end_of_data_ptr) |
Construct a VectorWithOffset with offset min_index pointing to existing data. More... | |
| VectorWithOffset (const int hsz, const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > *const data_ptr) | |
| Construct a VectorWithOffset of given length from a bare pointer (copying data) | |
| VectorWithOffset (const int min_index, const int max_index, const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > *const data_ptr) | |
Construct a VectorWithOffset with offset min_index from a bare pointer (copying data) | |
| VectorWithOffset (const int min_index, const int max_index, shared_ptr< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > []> data_sptr) | |
| Construct a VectorWithOffset sharing existing data. More... | |
| VectorWithOffset (const int sz, shared_ptr< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > []> data_sptr) | |
| Construct a VectorWithOffset sharing existing data. More... | |
| VectorWithOffset (const VectorWithOffset &il) | |
| copy constructor | |
| VectorWithOffset (VectorWithOffset &&other) noexcept | |
| move constructor More... | |
| virtual | ~VectorWithOffset () |
| Destructor. | |
| void | recycle () |
| Free all memory and make object as if default-constructed. More... | |
| VectorWithOffset & | operator= (const VectorWithOffset &il) |
| assignment operator with another vector More... | |
| Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > & | operator[] (int i) |
| allow array-style access, read/write More... | |
| const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > & | operator[] (int i) const |
| array access, read-only More... | |
| Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > & | at (int i) |
| allow array-style access, read/write, but with range checking (throws std::out_of_range) | |
| const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > & | at (int i) const |
| array access, read-only, but with range checking (throws std::out_of_range) | |
| bool | empty () const |
| checks if the vector is empty | |
| void | fill (const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > &n) |
| fill elements with value n | |
| void | apply_lower_threshold (const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > &lower) |
| Sets elements below value to the value. | |
| void | apply_upper_threshold (const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > &upper) |
| Sets elements above value to the value. | |
| int | get_length () const |
| return number of elements in this vector More... | |
| size_t | size () const |
| return number of elements in this vector | |
| int | get_min_index () const |
| get value of first valid index | |
| int | get_max_index () const |
| get value of last valid index | |
| void | set_offset (const int min_index) |
| change value of starting index | |
| void | set_min_index (const int min_index) |
| identical to set_offset() | |
| virtual void | grow (const int min_index, const int max_index) |
grow the range of the vector, new elements are set to T() More... | |
| void | grow (const unsigned int new_size) |
grow the range of the vector from 0 to new_size-1, new elements are set to T() | |
| virtual void | resize (const int min_index, const int max_index) |
change the range of the vector, new elements are set to T() More... | |
| void | resize (const unsigned int new_size) |
change the range of the vector from 0 to new_size-1, new elements are set to T() | |
| void | reserve (const int min_index, const int max_index) |
| make the allocated range at least from min_index to max_index | |
| void | reserve (const unsigned int new_size) |
| make the allocated range at least from 0 to new_size-1 | |
| size_t | capacity () const |
| get allocated size | |
| bool | owns_memory_for_data () const |
| check if this object owns the memory for the data More... | |
| int | get_capacity_min_index () const |
| get min_index within allocated range More... | |
| int | get_capacity_max_index () const |
| get max_index within allocated range More... | |
| bool | operator== (const VectorWithOffset &iv) const |
| bool | operator!= (const VectorWithOffset &iv) const |
| Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > * | get_data_ptr () |
| member function for access to the data via a T* More... | |
| const Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > * | get_const_data_ptr () const |
| member function for access to the data via a const T* More... | |
| void | release_data_ptr () |
| signal end of access to T* More... | |
| void | release_const_data_ptr () const |
| signal end of access to const T* More... | |
| iterator | begin () |
| use to initialise an iterator to the first element of the vector | |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| use to initialise an iterator to the first element of the (const) vector | |
| iterator | end () |
| iterator 'past' the last element of the vector | |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| iterator 'past' the last element of the (const) vector | |
| reverse_iterator | rbegin () |
| const_reverse_iterator | rbegin () const |
| reverse_iterator | rend () |
| const_reverse_iterator | rend () const |
| VectorWithOffset & | operator+= (const VectorWithOffset &v) |
adding elements of v to the current vector | |
| VectorWithOffset & | operator-= (const VectorWithOffset &v) |
subtracting elements of v from the current vector | |
| VectorWithOffset & | operator*= (const VectorWithOffset &v) |
multiplying elements of the current vector with elements of v | |
| VectorWithOffset & | operator/= (const VectorWithOffset &v) |
dividing all elements of the current vector by elements of v | |
| VectorWithOffset | operator+ (const VectorWithOffset &v) const |
| adding vectors, element by element | |
| VectorWithOffset | operator- (const VectorWithOffset &v) const |
| subtracting vectors, element by element | |
| VectorWithOffset | operator* (const VectorWithOffset &v) const |
| multiplying vectors, element by element | |
| VectorWithOffset | operator/ (const VectorWithOffset &v) const |
| dividing vectors, element by element | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static DiscretisedDensity * | read_from_file (const std::string &filename) |
| A static member to read an image from file. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual bool | actual_has_same_characteristics (DiscretisedDensity< num_dimensions, elemT > const &, std::string &explanation) const |
| Implementation used by has_same_characteristics. More... | |
| virtual CartesianCoordinate3D< float > | actual_get_relative_coordinates_for_indices (const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > &indices) const =0 |
| Implementation used by get_relative_coordinates_for_indices. More... | |
| virtual BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > | actual_get_index_coordinates_for_relative_coordinates (const CartesianCoordinate3D< float > &coords) const =0 |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > Protected Member Functions inherited from stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > | |
| void | check_state () const |
| Called internally to see if all variables are consistent. More... | |
| void | init_with_copy (const int min_index, const int max_index, Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > const *const data_ptr) |
change vector to the new index range and copy data from data_ptr More... | |
| void | init (const int min_index, const int max_index, Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > *const data_ptr, bool copy_data) |
initialise vector to the given index range and either copy from or point to data_ptr More... | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from stir::ExamData Protected Attributes inherited from stir::ExamData | |
| shared_ptr< const ExamInfo > | exam_info_sptr |
 Protected Attributes inherited from stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > Protected Attributes inherited from stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > > | |
| Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > * | num |
| pointer to (*this)[0] (taking get_min_index() into account that is). | |
Detailed Description
template<int num_dimensions, typename elemT>
class stir::DiscretisedDensity< num_dimensions, elemT >
This abstract class is the basis for all image representations.
This class is templated with the number of dimensions (should be 1, 2 or 3) and the type of the data.
It defines functionality common to all discretised densities: the data structure itself (Array) and an origin.
- Warning
- The origin is always a CartesianCoordinate3D<float>, independent of what coordinate system (or even dimension) this class represents. Similarly, the functions that translate from indices to physical coordinates assume that the later is 3D.
Iterative algorithms generally assume that the activity density can be discretised in some way. That is, the continuous density can be approximated by having a linear combination of some basis-functions. The reconstruction problem will try to estimate the coefficients 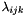 of the discretised density
of the discretised density
![\[ \sum_{ijk} \lambda_{ijk} b_{ijk}({\bar x}) \]](form_16.png)
The base class corresponding to this kind of data is DiscretisedDensity. We assume that the set of basisfunctions can be characterised by 3 indices (ijk) such that i runs over a range of integers i1..i2, j runs over a similar range that can however depend on i, and k runs over a similar range that can depend on i and j. This concept of ranges is embodied in the IndexRange class. Multi-dimensional arrays which have such ranges are encoded by the Array class. This forms the data structure for the set of coefficients of the basisfunctions, hence DiscretisedDensity is derived from the Array class.
In most useful cases, the basisfunctions will be translations of a single function b(x) (although scaling etc could occur depending on ijk). This means that the discretisation has a certain grid, corresponding to the centre of the basisfunctions. This structure is the next level in the image hierarchy. Currently we have the class DiscretisedDensityOnCartesianGrid to implement the case where the grid is formed by an orthogonal set of vectors. Another case would be e.g. DiscretisedDensityOnCylindricalGrid, but we have not implemented this yet.
The next level in the hierarchy is then finally the specification of the basis functions themselves. We currently have only voxels and pixels, but another useful case would be to use Kaiser-Bessel functions (so called Blobs). This leads us to the image hierarchy as shown in the class diagram.
Member Typedef Documentation
◆ hierarchy_base_type
| typedef DiscretisedDensity<num_dimensions, elemT> stir::DiscretisedDensity< num_dimensions, elemT >::hierarchy_base_type |
A typedef that can be used what the base of the hierarchy is.
For these purposes, we don't use Array (even though it's the base_type) as DiscretisedDensity is used in STIR as the type for any image.
This typedef is used in write_to_file().
Member Function Documentation
◆ read_from_file()
|
static |
A static member to read an image from file.
- Deprecated:
- This function just calls stir::read_from_file.
◆ get_physical_coordinates_for_indices() [1/2]
|
inline |
Return the coordinates of the centre of the basis-function corresponding to indices.
We distinguish between physical coordinates, relative coordinates (which are physical coordinates relative to the origin) and index coordinates (which run over the index range (but are allowed to have float values).
This class provides 3-way conversion functions. The derived classes have to implement the actual conversion between relative and index coordinates.
We distinguish also a fourth coordinate system, an LPS patient-based one. It is similar to the physical one, but the x (i.e. fastest-running) axis runs left-wards on the patient, the y-axis runs posterior-wards on the patient and the z-axis runs superior-wards on the patient. Conversion to this coordinate system depends on the patient position being recorded correctly. Only the most common patient positions are currently implemented.
The return value is in the same coordinate system as get_origin(). Implemented as
◆ get_physical_coordinates_for_indices() [2/2]
|
inline |
Return the coordinates of the centre of the basis-function corresponding to non-integer coordinate in 'physical' coordinates.
- See also
- get_physical_coordinates_for_indices(const BasicCoordinate<num_dimensions,int>&)
◆ get_relative_coordinates_for_indices() [1/2]
|
inline |
Return the relative coordinates of the centre of the basis-function corresponding to indices.
Implementation uses actual_get_relative_coordinates_for_indices
◆ get_relative_coordinates_for_indices() [2/2]
|
inline |
Return the relative coordinates of the centre of the basis-function corresponding to the non-integer coordinates in 'index' coordinates.
The return value is relative to the origin.
Implementation uses actual_get_relative_coordinates_for_indices
◆ get_indices_closest_to_physical_coordinates()
|
inline |
Return the indices of the basis-function closest to the given point.
The input argument should be in the same coordinate system as get_origin(). Implemented as
◆ get_indices_closest_to_relative_coordinates()
|
inline |
Return the indices of the basis-function closest to the given point.
The input argument should be in 'physical' coordinates relative to the origin. Implementation uses stir::round on the result of get_index_coordinates_for_relative_coordinates.
◆ get_index_coordinates_for_physical_coordinates()
|
inline |
Return the indices of the basis-function closest to the given point.
The input argument should be in 'physical' coordinates. Implementation uses get_index_coordinates_for_relative_coordinates.
◆ get_index_coordinates_for_relative_coordinates()
|
inline |
Return the index-coordinates of the basis-function closest to the given point.
The input argument should be in 'physical' coordinates relative to the origin. Implementation uses actual_get_index_coordinates_for_relative_coordinates.
◆ has_same_characteristics() [1/2]
|
inline |
Checks if the 2 objects have the same type, index range, origin etc.
If they do not have the same characteristics, the string explanation explains why.
Referenced by stir::LogcoshPrior< elemT >::accumulate_Hessian_times_input(), stir::QuadraticPrior< float >::accumulate_Hessian_times_input(), stir::GibbsPenalty< elemT, PotentialT >::accumulate_Hessian_times_input(), stir::RelativeDifferencePrior< elemT >::accumulate_Hessian_times_input(), stir::QuadraticPrior< float >::add_multiplication_with_approximate_Hessian(), stir::QuadraticPrior< float >::compute_gradient(), stir::LogcoshPrior< elemT >::compute_gradient(), stir::GibbsPenalty< elemT, PotentialT >::compute_gradient(), stir::RelativeDifferencePrior< elemT >::compute_gradient(), stir::GibbsPenalty< elemT, PotentialT >::compute_gradient_times_input(), stir::GibbsPenalty< elemT, PotentialT >::compute_Hessian(), stir::GibbsPenalty< elemT, PotentialT >::compute_Hessian_diagonal(), stir::BackProjectorByBin::get_output(), stir::QuadraticPrior< float >::parabolic_surrogate_curvature(), and stir::LogcoshPrior< elemT >::parabolic_surrogate_curvature().
◆ has_same_characteristics() [2/2]
|
inline |
Checks if the 2 objects have the same type, index range, origin etc.
Use this version if you do not need to know why they do not match.
◆ operator==()
|
inline |
check equality (data has to be identical)
Uses has_same_characteristics() and Array::operator==.
- Warning
- This function uses
==, which might not be what you need to check whenelemThas data with float or double numbers.
◆ actual_has_same_characteristics()
|
protectedvirtual |
Implementation used by has_same_characteristics.
- Warning
- Has to be overloaded by the derived classes to check for other parameters. Also, the overloaded function has to call the current one.
- Developer's note
We need this function as C++ rules say that if you overload a function, you hide all functions of the same name.
Reimplemented in stir::DiscretisedDensityOnCartesianGrid< num_dimensions, elemT >, stir::DiscretisedDensityOnCartesianGrid< 2, elemT >, and stir::DiscretisedDensityOnCartesianGrid< 3, elemT >.
◆ actual_get_relative_coordinates_for_indices()
|
protectedpure virtual |
Implementation used by get_relative_coordinates_for_indices.
- Developer's note
We need this function as C++ rules say that if you overload a function, you hide all functions of the same name.
Implemented in stir::DiscretisedDensityOnCartesianGrid< num_dimensions, elemT >, stir::DiscretisedDensityOnCartesianGrid< 2, elemT >, and stir::DiscretisedDensityOnCartesianGrid< 3, elemT >.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- /home/sirfuser/devel/STIRdistrib/STIR/src/include/stir/analytic/DDSR2D/DDSR2DReconstruction.h
- /home/sirfuser/devel/STIRdistrib/STIR/src/include/stir/DiscretisedDensity.h
- /home/sirfuser/devel/STIRdistrib/STIR/src/buildblock/DiscretisedDensity.cxx
- /home/sirfuser/devel/STIRdistrib/STIR/src/include/stir/DiscretisedDensity.inl
 1.8.13
1.8.13