Separable Metz filtering in n - dimensions.
More...
#include "stir/SeparableMetzArrayFilter.h"
Public Member Functions | |
| SeparableMetzArrayFilter () | |
| Default constructor. More... | |
| SeparableMetzArrayFilter (const VectorWithOffset< float > &fwhms, const VectorWithOffset< float > &metz_powers, const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > &sampling_distances, const VectorWithOffset< int > &max_kernel_sizes) | |
| Constructor. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from stir::SeparableArrayFunctionObject< num_dimensions, elemT > Public Member Functions inherited from stir::SeparableArrayFunctionObject< num_dimensions, elemT > | |
| SeparableArrayFunctionObject () | |
| Default constructor, results in a trivial ArrayFunctionObject. | |
| SeparableArrayFunctionObject (const VectorWithOffset< shared_ptr< ArrayFunctionObject< 1, elemT >>> &) | |
| Constructor taking 1D ArrayFunctionObjects. More... | |
| bool | is_trivial () const override |
| Should return true when the operations won't modify the object at all. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from stir::ArrayFunctionObject_1ArgumentImplementation< num_dimensions, elemT > Public Member Functions inherited from stir::ArrayFunctionObject_1ArgumentImplementation< num_dimensions, elemT > | |
| void | operator() (Array< num_dimensions, elemT > &array) const override |
| in-place modification More... | |
| void | operator() (Array< num_dimensions, elemT > &out_array, const Array< num_dimensions, elemT > &in_array) const override |
| result stored in another array, implemented inline | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from stir::ArrayFunctionObject< num_dimensions, elemT > Public Member Functions inherited from stir::ArrayFunctionObject< num_dimensions, elemT > | |
| virtual Succeeded | get_influencing_indices (IndexRange< num_dimensions > &influencing_indices, const IndexRange< num_dimensions > &output_indices) const |
| sets the range of indices that influences the result in a set of coordinates output_indices More... | |
| virtual Succeeded | get_influenced_indices (IndexRange< num_dimensions > &influenced_indices, const IndexRange< num_dimensions > &input_indices) const |
| sets the range of indices that gets influenced by a set of coordinate input_indices More... | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from stir::SeparableArrayFunctionObject< num_dimensions, elemT > Protected Member Functions inherited from stir::SeparableArrayFunctionObject< num_dimensions, elemT > | |
| void | do_it (Array< num_dimensions, elemT > &array) const override |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from stir::ArrayFunctionObject_1ArgumentImplementation< num_dimensions, elemT > Protected Member Functions inherited from stir::ArrayFunctionObject_1ArgumentImplementation< num_dimensions, elemT > | |
| virtual void | do_it (Array< num_dimensions, elemT > &array) const =0 |
 Protected Attributes inherited from stir::SeparableArrayFunctionObject< num_dimensions, elemT > Protected Attributes inherited from stir::SeparableArrayFunctionObject< num_dimensions, elemT > | |
| VectorWithOffset< shared_ptr< ArrayFunctionObject< 1, elemT > > > | all_1d_array_filters |
Detailed Description
template<int num_dimensions, typename elemT>
class stir::SeparableMetzArrayFilter< num_dimensions, elemT >
Separable Metz filtering in n - dimensions.
The Metz filter is easiest defined in frequency space. For a fwhm s and power P, its (continuous) Fourier transform is given by
![\[ M(k,s,P) = (1 - (1 - G(k, s)^2)^{(P + 1)})/ G(k, s) \]](form_149.png)
where 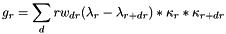 is the Fourier transform of a Gaussian with FWHM
is the Fourier transform of a Gaussian with FWHM s, normalised such that 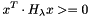 .
.
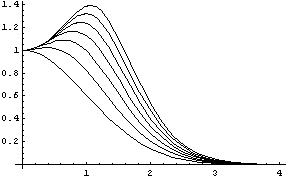
For power 0, the Metz filter is just a Gaussian. For higher power, mid-range frequencies are more and more amplified. The first figure shows the FT of the Metz filter with fwhm 1, for powers 0, 0.5, 1, ... 3 (lowest curve is Gaussian).
Spatially, the Metz filter has negative lobes. The 2nd figure shows the Metz kernel in space, again with fwhm 1, powers 0 (long dashes),1,2,3 (no dashes)
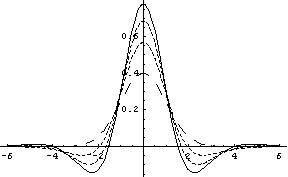
![\[ Metz(x,s,P) = Metz(x/s, 1 ,P)/s \]](form_152.png)
The final figure illustrates the relation between the actual FWHM of the Metz filter and the FWHM of the underlying Gaussian.
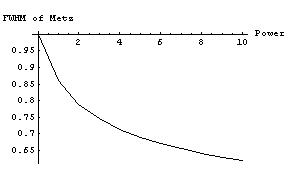
This implementation discretises the Metz filter currently in the following way. it assumes that the input data are band-limited. For such data, it is possible to compute the filtering with the continuous Metz filter exactly. This is done with linear convolution of the sampled data with samples of the spatial Metz cut off at the same frequency as the input data.
- Warning
- Currently, this implements a Metz filter cut off at 1/
sampling_distance. - The Metz filter does not preserve positivity.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ SeparableMetzArrayFilter() [1/2]
|
inline |
Default constructor.
- Warning
- This currently does not set things properly for a trivial filter.
◆ SeparableMetzArrayFilter() [2/2]
| stir::SeparableMetzArrayFilter< num_dimensions, elemT >::SeparableMetzArrayFilter | ( | const VectorWithOffset< float > & | fwhms, |
| const VectorWithOffset< float > & | metz_powers, | ||
| const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, float > & | sampling_distances, | ||
| const VectorWithOffset< int > & | max_kernel_sizes | ||
| ) |
Constructor.
- Parameters
-
fwhms the FWHM of the underlying Gauss 1D filters (in mm) metz_powers the powers of the 1D Metz filters sampling_distances in each dimensions (in mm) max_kernel_sizes maximum number of elements in the kernels. -1 means unrestricted
For each of these parameters, the index range should be from 1 to num_dimensions, with 1 corresponding to the 1st (i.e. slowest) index.
- Warning
- the fwhms parameter does
notgive the FWHM of the Metz filter, but of the underlying Gauss.
References stir::Array< num_dimensions, elemT >::fill(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::fill(), stir::fourier(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::get_length(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::get_min_index(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::grow(), stir::info(), stir::inverse_fourier(), and stir::sum().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- /home/sirfuser/devel/STIRdistrib/STIR/src/include/stir/SeparableMetzArrayFilter.h
- /home/sirfuser/devel/STIRdistrib/STIR/src/buildblock/SeparableMetzArrayFilter.cxx
 1.8.13
1.8.13