|
Modules | |
| Discrete Fourier transforms | |
| Classes and functions for B-spline interpolation. | |
Files | |
| file | determinant.h |
| Declaration of stir::determinant() function for matrices. | |
| file | divide.h |
| implementation of stir::divide | |
| file | divide.inl |
| implementation of stir::divide | |
| file | erf.h |
| file | FastErf.h |
| Implementation of an erf interpolation. | |
| file | FastErf.inl |
| Implementation of an erf interpolation. | |
| file | fftshift.h |
| Functions to rearrange Fourier data so that DC (zero frequency) is centered. | |
| file | ieeefp.h |
| Definition of work-around macros STIR_isnan and STIR_finite for a few non-portable IEEE floating point functions. | |
| file | integrate_discrete_function.h |
| Declaration of stir::integrate_discrete_function function. | |
| file | IR_filters.h |
| Implementation of the IIR and FIR filters. | |
| file | IR_filters.inl |
| implements the IR_filters | |
| file | MatrixFunction.h |
| Declaration of functions for matrices. | |
| file | MatrixFunction.inl |
| Implementation of functions for matrices. | |
| file | max_eigenvector.h |
| Declaration of functions for computing eigenvectors. | |
| file | norm.h |
| Declaration of the stir::norm(), stir::norm_squared() functions and stir::NormSquared unary function. | |
| file | norm.inl |
| Implementation of the stir::norm(), stir::norm_squared() functions and stir::NormSquared unary function. | |
| file | overlap_interpolate.h |
| Declaration of stir::overlap_interpolate. | |
| file | overlap_interpolate.inl |
| Implementation of inline versions of stir::overlap_interpolate. | |
| file | sampling_functions.h |
| Sampling functions (currently only stir::sample_function_on_regular_grid) | |
| file | stir_NumericalRecipes.h |
| functions to convert from data in Numerical Recipes format to STIR arrays. | |
| file | linear_extrapolation.h |
| stir::linear_extrapolation | |
| file | more_interpolators.h |
| Functions to interpolate data. | |
| file | more_interpolators.inl |
| Functions to interpolate data. | |
| file | determinant.cxx |
| Implementation of stir::determinant() function for matrices. | |
Namespaces | |
| stir | |
| Namespace for the STIR library (and some/most of its applications) | |
Classes | |
| class | stir::PullLinearInterpolator< elemT > |
| A function object to pull interpolated values from the input array into the grid points of the output array. More... | |
| class | stir::PushTransposeLinearInterpolator< elemT > |
| A function object to push values at the grid of the input array into the output array. More... | |
| class | stir::PullNearestNeighbourInterpolator< elemT > |
| A function object to pull interpolated values from the input array into the grid points of the output array. More... | |
| class | stir::PushNearestNeighbourInterpolator< elemT > |
| A function object to push values at the grid of the input array into the output array. More... | |
Functions | |
| template<class elemT > | |
| elemT | stir::determinant (const Array< 2, elemT > &m) |
| Compute the determinant of a matrix. More... | |
| template<class NumeratorIterT , class DenominatorIterT , class small_numT > | |
| void | stir::divide (const NumeratorIterT &numerator_begin, const NumeratorIterT &numerator_end, const DenominatorIterT &denominator_begin, const small_numT small_num) |
| division of two ranges, 0/0 = 0 More... | |
| template<typename elemT > | |
| elemT | stir::integrate_discrete_function (const std::vector< elemT > &coordinates, const std::vector< elemT > &values, const int interpolation_order=1) |
| numerical integration of a 1D functionThis is a simple integral implementation using rectangular (=0) or trapezoidal (=1) approximation. It currently integrates over the complete range specified. More... | |
| template<class elemT > | |
| Succeeded | stir::absolute_max_eigenvector_using_power_method (elemT &max_eigenvalue, Array< 1, elemT > &max_eigenvector, const Array< 2, elemT > &m, const Array< 1, elemT > &start, const double tolerance=.01, const unsigned long max_num_iterations=10000UL) |
| Compute the eigenvalue with the largest absolute value and corresponding eigenvector of a matrix by using the power method. More... | |
| template<class elemT > | |
| Succeeded | stir::absolute_max_eigenvector_using_shifted_power_method (elemT &max_eigenvalue, Array< 1, elemT > &max_eigenvector, const Array< 2, elemT > &m, const Array< 1, elemT > &start, const elemT shift, const double tolerance=.03, const unsigned long max_num_iterations=10000UL) |
| Compute the eigenvalue with the largest absolute value and corresponding eigenvector of a matrix by using the shifted power method. More... | |
| template<class elemT > | |
| Succeeded | stir::max_eigenvector_using_power_method (elemT &max_eigenvalue, Array< 1, elemT > &max_eigenvector, const Array< 2, elemT > &m, const Array< 1, elemT > &start, const double tolerance=.03, const unsigned long max_num_iterations=10000UL) |
| Compute the eigenvalue with the largest value and corresponding eigenvector of a matrix by using the power method. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | stir::overlap_interpolate (VectorWithOffset< T > &out_data, const VectorWithOffset< T > &in_data, const float zoom, const float offset, const bool assign_rest_with_zeroes=true) |
| 'overlap' interpolation (i.e. count preserving) for vectors. More... | |
| template<typename out_iter_t , typename out_coord_iter_t , typename in_iter_t , typename in_coord_iter_t > | |
| void | stir::overlap_interpolate (const out_iter_t out_begin, const out_iter_t out_end, const out_coord_iter_t out_coord_begin, const out_coord_iter_t out_coord_end, const in_iter_t in_begin, in_iter_t in_end, const in_coord_iter_t in_coord_begin, const in_coord_iter_t in_coord_end, const bool only_add_to_output=false, const bool assign_rest_with_zeroes=true) |
| 'overlap' interpolation for iterators, with arbitrary 'bin' sizes. More... | |
| template<class FunctionType , class elemT , class positionT > | |
| void | stir::sample_function_on_regular_grid (Array< 3, elemT > &out, FunctionType func, const BasicCoordinate< 3, positionT > &offset, const BasicCoordinate< 3, positionT > &step) |
| Generic function to get the values of a 3D function on a regular grid. More... | |
| template<typename elemT , typename FunctionType , typename Lambda > | |
| void | stir::sample_function_using_index_converter (Array< 3, elemT > &out, FunctionType func, Lambda &&index_converter) |
| Generic function to get the values of a 3D function on a grid. More... | |
| template<class elemT , class positionT > | |
| elemT | stir::pull_nearest_neighbour_interpolate (const Array< 3, elemT > &in, const BasicCoordinate< 3, positionT > &point_in_input_coords) |
| Pull value from the input array using nearest neigbour interpolation. More... | |
| template<int num_dimensions, class elemT , class positionT , class valueT > | |
| void | stir::push_nearest_neighbour_interpolate (Array< num_dimensions, elemT > &out, const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, positionT > &point_in_output_coords, valueT value) |
| Push value into the output array using nearest neigbour interpolation. More... | |
| template<class elemT , class positionT > | |
| elemT | stir::pull_linear_interpolate (const Array< 3, elemT > &in, const BasicCoordinate< 3, positionT > &point_in_input_coords) |
| Returns an interpolated value according to point_in_input_coords. | |
| template<class elemT , class positionT , class valueT > | |
| void | stir::push_transpose_linear_interpolate (Array< 3, elemT > &out, const BasicCoordinate< 3, positionT > &point_in_output_coords, valueT value) |
| Push value into the output array using the transpose of linear interpolation. | |
| Array< 3, float > | stir::extend_segment (const SegmentBySinogram< float > &segment, const int view_extension=5, const int axial_extension=5, const int tangential_extension=5) |
| Extension of direct projection data. More... | |
functions specific for 1D Arrays | |
| template<class elemT > | |
| elemT | stir::inner_product (const Array< 1, elemT > &v1, const Array< 1, elemT > &v2) |
| Inner product of 2 1D arrays. More... | |
| template<class elemT > | |
| double | stir::angle (const Array< 1, elemT > &v1, const Array< 1, elemT > &v2) |
| angle between 2 1D arrays | |
Detailed Description
Function Documentation
◆ extend_segment()
| Array< 3, float > stir::extend_segment | ( | const SegmentBySinogram< float > & | segment, |
| const int | view_extension = 5, |
||
| const int | axial_extension = 5, |
||
| const int | tangential_extension = 5 |
||
| ) |
Extension of direct projection data.
Functions that extend the given sinogram or segment in the view direction taking periodicity into account, if exists. If the sinogram is not symmetric in tangential position, the values are extrapolated by nearest neighbour known values.
This is probably only useful before calling interpolation routines, or for FORE.
Generic function to extend a segment in any or all directions. Axially and tangentially, the segment is filled with the nearest existing value. In view direction, the function wraps around for stir::ProjData that cover 180° or 360° degrees, and throws an error for other angular coverages.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] segment segment to be extended. [in] view_extension how many views to add either side of the segment [in] axial_extension how many axial bins to add either side of the segment [in] tangential_extension how many tangential bins to add either side of the segment
References _PI, stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > >::get_max_index(), stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > >::get_min_index(), stir::Segment< elemT >::get_proj_data_info_sptr(), and stir::Array< num_dimensions, elemT >::grow().
◆ determinant()
| elemT stir::determinant | ( | const Array< 2, elemT > & | m | ) |
Compute the determinant of a matrix.
Matrix indices can start from any number.
- Todo:
- Only works for low dimensions for now.
Referenced by stir::Shape3DWithOrientation::get_volume_of_unit_cell().
◆ divide()
|
inline |
division of two ranges, 0/0 = 0
This function sets 0/0 to 0 (not the usual NaN). It is for instance useful in Poisson log-likelihood computation.
Because of potential numerical rounding problems, we test if a number is 0 by comparing its absolute value with a small value, which is determined by multiplying the maximum in the numerator range with small_num.
- Warning
- This function does not test for non-zero numbers by 0. Results in that case will likely depend on your processor and/or compiler settings.
Referenced by stir::BinNormalisationPETFromComponents::apply().
◆ integrate_discrete_function()
|
inline |
numerical integration of a 1D functionThis is a simple integral implementation using rectangular (=0) or trapezoidal (=1) approximation. It currently integrates over the complete range specified.
- Parameters
-
coordinates Coordinates at which the function samples are given values Function values interpolation_order has to be 0 or 1
- Warning
- Type
elemTshould not be an integral type.
Referenced by stir::PlasmaData::get_sample_data_in_frames(), and stir::integrate_discrete_functionTests::run_tests().
◆ inner_product()
|
inline |
Inner product of 2 1D arrays.
This returns the sum of multiplication of elements of conjugate(v1) and v2.
Implementation is appropriate for complex numbers.
Arguments must have the same index range.
◆ absolute_max_eigenvector_using_power_method()
|
inline |
Compute the eigenvalue with the largest absolute value and corresponding eigenvector of a matrix by using the power method.
- Parameters
-
[out] max_eigenvalue will be set to the eigenvalue found [out] max_eigenvector will be set to the eigenvector found, and is normalised to 1 (using the l2-norm). The sign choice is determined by normalising the largest element in the eigenvector to 1. [in] m is the input matrix [in] start is a starting vector for the iterations [in] tolerance determines when iterations can stop [in] max_num_iterations is used to prevent an infinite loop
- Returns
- Succeeded::yes if max_num_iterations was not reached. However, you probably want to check if the norm of the difference between
m.max_eigenvectorandmax_eigenvalue*max_eigenvectoris small (compared to max_eigenvalue).
Computation uses the power method, see for instance http://www.maths.lth.se/na/courses/FMN050/FMN050-05/eigenE.pdf.
The method consists in computing
![\[v^{n+1}=m.v^{n}\]](form_40.png)
![\[v^{n+1}/=\mathrm{norm}(v^{n+1})\]](form_41.png)
with 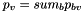 for
for 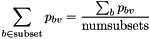 big enough such that
big enough such that 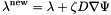 becomes smaller than tolerance. The eigenvalue is then computed using the Rayleigh quotient
becomes smaller than tolerance. The eigenvalue is then computed using the Rayleigh quotient
![\[v.m.v \over v.v \]](form_45.png)
This will converge to the eigenvector which has the largest absolute eigenvalue. The method fails when the matrix has more than 1 largest absolute eigenvalue (e.g. with opposite sign).
References stir::abs_max_element(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::begin(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::end(), stir::inner_product(), stir::Array< num_dimensions, elemT >::is_regular(), stir::matrix_multiply(), stir::norm(), stir::norm_squared(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::size(), and stir::square().
Referenced by stir::absolute_max_eigenvector_using_shifted_power_method(), and stir::max_eigenvector_using_power_method().
◆ absolute_max_eigenvector_using_shifted_power_method()
|
inline |
Compute the eigenvalue with the largest absolute value and corresponding eigenvector of a matrix by using the shifted power method.
The current method calls the normal power method for m-shift*I and shifts the eigenvalue back to the eigenvalue for m.
This method can be used to enhance the convergence rate if you know more about the eigenvalues. It can also be used to find another eigenvalue by shifting with the maximum eigenvalue.
References stir::absolute_max_eigenvector_using_power_method(), stir::diagonal_matrix(), stir::error(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::get_min_index(), and stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::size().
Referenced by stir::max_eigenvector_using_power_method().
◆ max_eigenvector_using_power_method()
|
inline |
Compute the eigenvalue with the largest value and corresponding eigenvector of a matrix by using the power method.
- Warning
- This assumes that all eigenvalues are real.
- Parameters
-
[in] m is the input matrix, which has to be real-symmetric
This will attempt to find the eigenvector which has the largest eigenvalue. The method fails when the matrix has a negative eigenvalue of the same magnitude as the largest eigenvalue.
- Todo:
- the algorithm would work with hermitian matrices, but the code needs one small adjustment.
References stir::absolute_max_eigenvector_using_power_method(), and stir::absolute_max_eigenvector_using_shifted_power_method().
Referenced by stir::RigidObject3DTransformation::find_closest_transformation().
◆ overlap_interpolate() [1/2]
| void stir::overlap_interpolate | ( | VectorWithOffset< T > & | out_data, |
| const VectorWithOffset< T > & | in_data, | ||
| const float | zoom, | ||
| const float | offset, | ||
| const bool | assign_rest_with_zeroes | ||
| ) |
'overlap' interpolation (i.e. count preserving) for vectors.
This is an implementation of 'overlap' interpolation on arbitrary data types (using templates).
This type of interpolation considers the data as the samples of a step-wise function. The interpolated array again represents a step-wise function, such that the counts (i.e. integrals) are preserved.
- Parameters
-
zoom The spacing between the new points is determined by the 'zoom' parameter: e.g. zoom less than 1 stretches the bin size with a factor 1/zoom. offset (measured in 'units' of the in_data) allows to shift the range of values you want to compute. In particular, having positive offset shifts the data to the left (if in_data and out_data have the same range of indices). Note that a similar (but less general) effect to using 'offset' can be achieved by adjusting the min and max indices of the out_data. assign_rest_with_zeroes If falsedoes not set values inout_datawhich do not overlap within_data. Iftruethose data are set to 0. (The effect being the same as first doingout_data.fill(0)before calling overlap_interpolate).
For an index x_out (in out_data coordinates), the corresponding in_data coordinates is x_in = x_out/zoom + offset (The convention is used that the 'bins' are centered around the coordinate value.)
- Warning
- when T involves integral types, there is no rounding but truncation.
- Examples:
in_data = {a,b,c,d} indices from 0 to 3
zoom = .5
offset = .5
out_data = {a+b, c+d} indices from 0 to 1
in_data = {a,b,c,d} indices from 0 to 3
zoom = .5
offset = -.5
out_data = {a,b+c,d} indices from 0 to 2
in_data = {a,b,c} indices from -1 to 1
zoom = .5
offset = 0
out_data = {a/2, a/2+b+c/2, c/2} indices from -1 to 1
- Implementation details:
Because this implementation works for arbitrary (numeric) types T, it is slightly more complicated than would be necessary for (say) floats. In particular,
- we do our best to avoid creating temporary objects of type T
- we zero values by using multiplication with 0
(actually we use T::operator*=(0)). This is to allow the case where T::operator=(int) does not exist (in particular, in our higher dimensional arrays).
- History:
- first version by Kris Thielemans with suggestions by Alexey Zverovich. (loosely based on a 1D version by Claire Labbe)
- See also
- overlap_interpolate(const out_iter_t out_begin, const out_iter_t out_end, const out_coord_iter_t out_coord_begin, const out_coord_iter_t out_coord_end, const in_iter_t in_begin, in_iter_t in_end, const in_coord_iter_t in_coord_begin, const in_coord_iter_t in_coord_end, const bool only_add_to_output=false, const bool assign_rest_with_zeroes)
Referenced by stir::ArcCorrection::set_up(), and stir::zoom_image().
◆ overlap_interpolate() [2/2]
|
inline |
'overlap' interpolation for iterators, with arbitrary 'bin' sizes.
This type of interpolation considers the data as the samples of a step-wise function. The interpolated array again represents a step-wise function, such that the counts (i.e. integrals) are preserved.
In and out data are specified using iterators. For each, there is also a pair of iterators specifying the coordinates of the edges of the 'bins' (or 'boxes') in some arbitrary coordinate system (common between in and out parameters of course). Note that there should be one more coordinate than data (i.e. you have to specify the last edge as well). This is (only) checked with assert() statements.
- Parameters
-
only_add_to_output If falsewill overwrite any data present in the output (aside from possibly the tails: seeassign_rest_with_zeroes). Iftrue, results will be added to the data.assign_rest_with_zeroes If falsedoes not set values in theoutrange which do not overlap withinrange. Iftruethose data are set to 0.
- Warning
- when the out iterators point to an integral type, there is no rounding but truncation.
- Examples:
- Given 2 arrays and zoom and offset parameters the following pieces of code should give the same result (this is tested in test_interpolate):Array<1,float> in = ...;Array<1,float> out = ...;float zoom = ...; float offset = ...;andoverlap_interpolate(out, in, zoom, offset, true);Array<1,float> in_coords(in.get_min_index(), in.get_max_index()+1);for (int i=in_coords.get_min_index(); i<=in_coords.get_max_index(); ++i)in_coords[i]=i-.5F;Array<1,float> out_coords(out.get_min_index(), out.get_max_index()+1);for (int i=out_coords.get_min_index(); i<=out_coords.get_max_index(); ++i)out_coords[i]=(i-.5F)/zoom+offset;overlap_interpolate(out.begin(), out.end(),out_coords.begin(), out_coords.end(),in.begin(), in.end(),in_coords.begin(), in_coords.end());
- Implementation details:
Because this implementation works for arbitrary (numeric) types, it is slightly more complicated than would be necessary for (say) floats. In particular,
- we do our best to avoid creating temporary objects
- we zero values by using multiplication with 0. This is to allow the case where assignment with an int (or float) does not exist (in particular, in our higher dimensional arrays).
The implementation is inline to avoid problems with template instantiations.
- History:
- first version by Kris Thielemans
◆ sample_function_on_regular_grid()
|
inline |
Generic function to get the values of a 3D function on a regular grid.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] out array that will be filled with the function values. Its dimensions are used to find the coordinates where to sample the function (see below). [in] func function to sample [in] offset offset to use for coordinates (see below) [in] step step size to use for coordinates (see below)
Symbolically, this function does the following computation for every index in the array
- requirement for type FunctionType
- Due to the calling sequence above, the following has to be defined elemT FunctionType::operator(const BasicCoordinate<3, positionT>&)
- Todo:
- At the moment, only the 3D version is implemented, but this could be templated.
References stir::IndexRange< num_dimensions >::get_regular_range(), and stir::warning().
◆ sample_function_using_index_converter()
|
inline |
Generic function to get the values of a 3D function on a grid.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] out array that will be filled with the function values. Its dimensions are used to find the coordinates where to sample the function (see below). [in] func function to sample [in] index_converter a lambda function converting indices in the out array to coordinates where the function shall be sampled
- requirement for type FunctionType
- Due to the calling sequence above, the following has to be defined elemT FunctionType::operator(const BasicCoordinate<3, positionT>&)
- Todo:
- At the moment, only the 3D version is implemented, but this could be templated.
References stir::IndexRange< num_dimensions >::get_regular_range(), and stir::warning().
◆ pull_nearest_neighbour_interpolate()
| elemT stir::pull_nearest_neighbour_interpolate | ( | const Array< 3, elemT > & | in, |
| const BasicCoordinate< 3, positionT > & | point_in_input_coords | ||
| ) |
Pull value from the input array using nearest neigbour interpolation.
Adds value to the grid point nearest to point_in_output_coords
References stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::get_max_index(), stir::VectorWithOffset< T >::get_min_index(), and stir::round().
◆ push_nearest_neighbour_interpolate()
| void stir::push_nearest_neighbour_interpolate | ( | Array< num_dimensions, elemT > & | out, |
| const BasicCoordinate< num_dimensions, positionT > & | point_in_output_coords, | ||
| valueT | value | ||
| ) |
Push value into the output array using nearest neigbour interpolation.
Adds value to the grid point nearest to point_in_output_coords
References stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > >::get_max_index(), stir::VectorWithOffset< Array< num_dimensions - 1, elemT > >::get_min_index(), and stir::round().
 1.8.13
1.8.13